Introduction to the differences between gray light Modules and color light Modules
Time: 2023-12-13
⦁ Background
We often hear about gray light module and color light module, what are the differences in their characteristics and applications? The following is a brief chat.
⦁ Wavelength window for optical communication
The first window of 850nm, the second window of 1310nm, the third window of 1550nm and the fourth window of 1625nm are used for optical communication, as shown in the figure below:
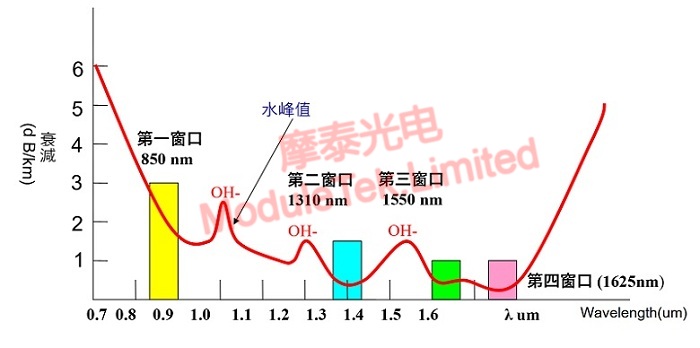
Figure 1 Wavelength windows for optical communication and attenuation in optical fiber
From the above figure, it can be seen that the wavelength for optical communication is mainly 850-1625nm, while the wavelength of light visible to the naked eye (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue and purple) is mainly distributed in the 780-380nm, so the gray and colored light module does not mean that the light module emits a gray or colored.
⦁ Definition and difference between gray and colored light modules
Gray light module (Grey): the wavelength is fluctuating within a certain range, there is no specific standard wavelength, such as the customer side of the wavelength division equipment optical port, the corresponding interface is called gray light interface.
Color light module (Color): wavelength fluctuations in a very small range near the center wavelength, can be connected to the combined wave device, with a standard wavelength, wavelength division system in the line veneer wavelength division side of the optical signal, the corresponding interface is called a color light interface.
Color optical module according to the different wavelength density can be divided into CWDM (coarse wavelength division multiplexing) optical module and DWDM (dense wavelength division multiplexing) optical module, color optical module ride with the wavelength of the wave will be synthesized with different wavelengths of the optical signal all the way to transmission, greatly reducing the link cost.
The following figure briefly describes the application scenarios of gray light and color light modules:
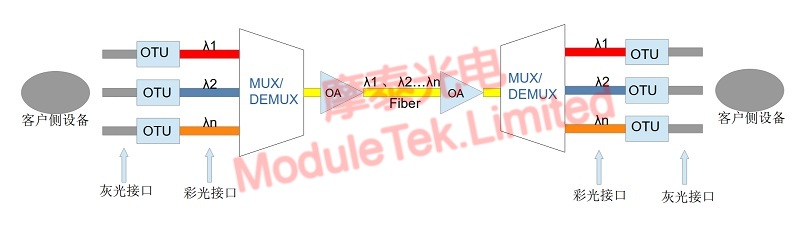
Figure 2 gray light and color light module application scenarios
A brief summary of the differences between gray light and color light modules, the following table:
Table 1 gray light and color light module differences
|
Optical module type
|
Gray Optical module
|
Color Optical module
|
|
Wavelength
|
Center wavelength range: approximately ±30nm
|
CWDM center wavelength range: ±6.5nm DWDM/100GHZ center wavelength range: ±0.04nm
|
|
Application
|
Mostly used on the customer side
|
Mostly used on the line side
|
|
Characteristics
|
Low power consumption, suitable for short-distance transmission
|
Large bandwidth capacity, saving fiber resources
|
|
Standard Compliance
|
ITU-T G.957 ITU-T G.959.1 IEEE802.3
|
ITU-T G.694.1(DWDM)ITU-T G694.2(CWDM)
|
|
Product Example
|
SFP-OC3-IR1
SFP-GE-SX
SFP-10G-LR
SFP28-25G-SR
|
SFP-GE-CWDM-1470
SFP-10G-ZR-CWDM-1550
SFP-10G-ZR-DWDM-P57-1531.90
SFP28-25G-LR-CWDM-1330
|
Moduletek limited is at your service !
If you have any questions about the above content, please contact us via email: sales@moduletek.com
 40G/100G Optical Transceivers
40G/100G Optical Transceivers 10G/25G Optical Transceivers
10G/25G Optical Transceivers 155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers
155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers 1G Optical Transceivers
1G Optical Transceivers FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers
FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers
CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers SGMII Port Optical Transceivers
SGMII Port Optical Transceivers 100M/1G/10G Coppers
100M/1G/10G Coppers Active Cable AOC
Active Cable AOC Direct Attach Cable DAC
Direct Attach Cable DAC Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords
Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords MT2011
MT2011 MT2010
MT2010 CodingBox
CodingBox QSFP to SFP Adapter
QSFP to SFP Adapter






