Why Do Fiber Optic Connectors Fail?
Time: 2020-02-23
Fiber optic connectors are designed for high-speed fiber optic links. High-loss fiber optic connectors can result in network outages, which is something we all want to avoid. Issues related to the end-face quality and performance of fiber optic patch cords may cause network faults that are often difficult to troubleshoot. Let us take a closer look at the relevant information about fiber optic connector failures.
1. What Are the Common Fiber Optic Connector Failures?
Failures of fiber optic connectors may be related to ferrules, such as cracks, chips, slight bending, breakage or micro-fractures inside the ferrule. In addition to these ferrule-related problems, failures can also be associated with the optical fiber itself, which may result from improper assembly processes like excessive/insufficient epoxy resin or air bubbles in the adhesive, as well as improper stripping or coiling processes.
2. Three Main Causes of Fiber Optic Connector Failures
Problem 1: Contaminated End-Faces
Problems Caused:
1. Poor light transmission or a complete loss of light propagation
2. Light reflection back to the connection point and transmission source, leading to device malfunction
Contaminants:

Figure 1: Dust
Figure 2: Oil Stains

Figure 3: Fiber Fragments
Root Cause: When contaminants are present on the fiber optic end-face, light may fail to pass through the surface, resulting in degraded loss performance of the fiber optic connector.
Solution: Inspect and clean the end-faces repeatedly to ensure they are free of contaminants before mating.

Figure 4: Clean End-Face
Problem 2: Exceeding the Bend Radius
Problems Caused:
1. Exceeding the allowable bend radius, leading to high signal loss
2. Significant degradation in overall link loss performance
Root Cause: Excessive bending of the fiber optic cable causes fiber attenuation, which we refer to as macrobending loss. This usually occurs during the installation process.
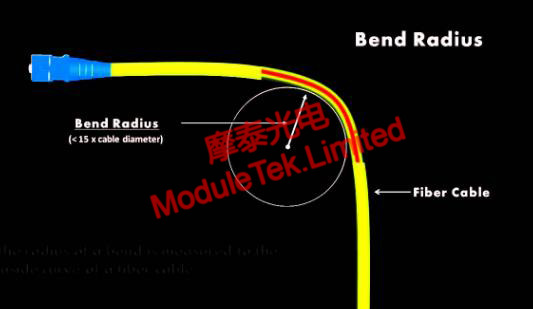
Figure 5: Fiber Optic Cable Bend Radius
Solution: Bend the cable appropriately in accordance with the cable bend tolerance specifications provided by the supplier. If the installation environment requires cable bends beyond the minimum bend radius, it is recommended to use bend-insensitive optical fibers, which typically have a minimum bend radius of 10mm.
Problem 3: Misalignment
Problems Caused:
1. High insertion loss
2. Significant degradation in overall link loss performance
Root Cause: Excessive insertion loss is usually caused by fiber misalignment and fiber material mismatch, which involves both external and internal factors:
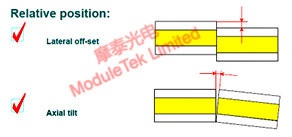
Figure 6: External Cause: Poor Ferrule Mating
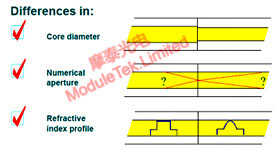
Figure 7: Internal Cause: Fiber Material Mismatch
Solution: Purchase high-quality components from reliable component manufacturers.
Moduletek offers high-quality fiber optic connector products. Feel free to contact us for product inquiries and orders.
If you have any questions about the above content, please contact us via email: sales@moduletek.com
 40G/100G Optical Transceivers
40G/100G Optical Transceivers 10G/25G Optical Transceivers
10G/25G Optical Transceivers 155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers
155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers 1G Optical Transceivers
1G Optical Transceivers FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers
FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers
CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers SGMII Port Optical Transceivers
SGMII Port Optical Transceivers 100M/1G/10G Coppers
100M/1G/10G Coppers Active Cable AOC
Active Cable AOC Direct Attach Cable DAC
Direct Attach Cable DAC Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords
Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords MT2011
MT2011 MT2010
MT2010 CodingBox
CodingBox QSFP to SFP Adapter
QSFP to SFP Adapter






